Product Description
Service
Why choose us?
Buyers review
1. Stock view
2. Processing and Technology for heating processing
Cutting processing Quenching Tempering Annealing
3. Quality testing
1. Inspection Institution
Shanghai Fuda Testing Technology Group Co., LTD. Nanjing Branch
Focus on analysis, testing, testing, r & D four service areas. Analysis fields include component analysis, formula analysis, failure analysis, structure analysis, methodology development and validation, raw material quality control/evaluation, consistency evaluation, feature analysis and other directions; The testing field involves physical and chemical properties testing, toxic and harmful substances testing, flame retardant performance testing, reliability testing and other directions; The testing field involves energy spectrum, electron microscope, spectrum, chromatography, mass spectrometry and other directions; The r&d field involves formula development, formula upgrading, formula customisation, cooperative research and development and other directions.
Beijing Zhongke Chemical Technology Research Institute
It is a chemical technology research institution based on scientific research and testing. They adhere to paying equal attention to basic research and applied research, and combining applied research and technology transformation, developing into a comprehensive research institute characterised by "task-oriented disciplines". Approved by the relevant national departments, the company has become a third-party analysis and testing technology service unit, and has obtained CMA qualification certification. It has carried out research and development and design, analysis and testing, test and verification, generic processing, information and intellectual property services, providing public services for innovation of technology-based enterprises. Supported by the government innovation Fund, the institute has been awarded as a national high-tech enterprise.



2.Inspection Machining
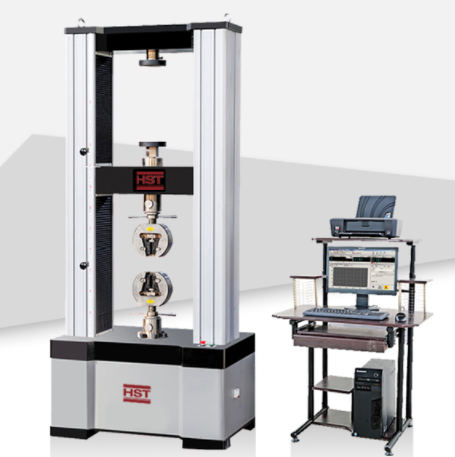



Metal composition testing machine Computerised Materials Torsion Testing Machine Metal bar composite rod bending tensile strength testing machine
3. Material test certificate
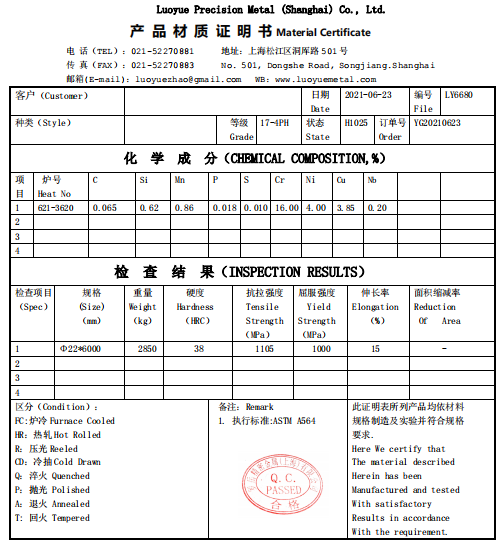
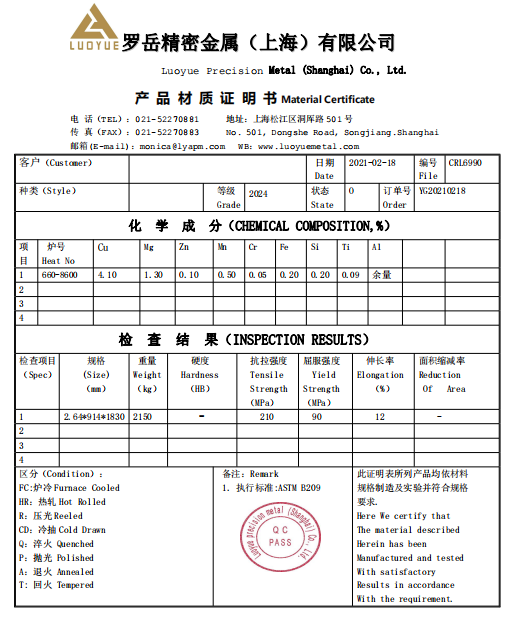
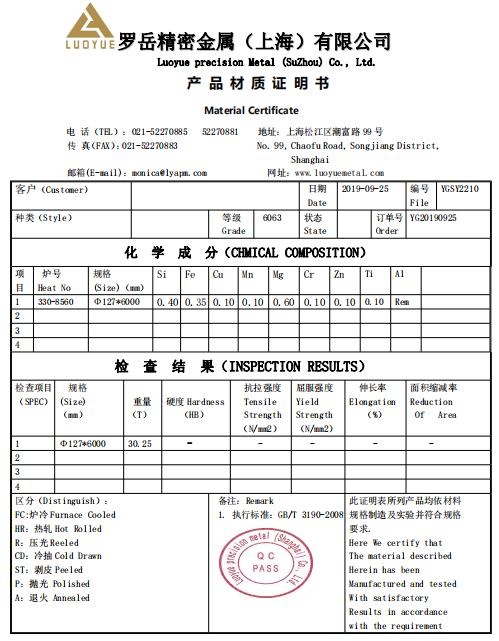
4. Packaging
In the steel export activities, we also need to pack the steel to prevent the steel from being scattered in the transportation process. In the hoisting process, it is necessary to lift the steel. So steel is very necessary in the export process. Below is the picture of packaging:



According to the requirements of the state of steel materials, the use of binding, bare, frame, pallet.
Packing standard: according to the following national standard requirements (the parts beyond the requirements will be specified separately)
GB/T191 packaging-pictorial marking for handling of goods
GB/T4857 (all parts) basic test for transport packages
GB/T4879 rustproof packaging
GB/T5048 damp-proof packing
GB/T7350water-proof packing
GB/T8166 Package cushioning design
GB/T4892-1996 Hard straight square transport packaging size series
GB/T13201-91 Cylinder transport package size series
GB/T16471-1996Design and make the size limit of transport package
5. Logistic



1. Company profile
Luoyue Precision Metal established in 2018, is a leading Stockists and global distributor for Metal Raw Materials like Steel/Aluminum/ Stainless steel/Copper/ Nickel Rods, Bars, Plates, Sheets,Pipes, fittings, fasteners, Inconel alloys, Wire and Wire-Mesh to customers from aerospace, automotive, electronics, precision manufacturing, ordnance, marine, shipbuilding, oil & gas, power plant and construction.
The company has a high-precision, high-efficiency modern processing site, CNC machine tools and complete testing and inspection technology, and introduces international advanced technologies.


2. Certificates. (Business certificate/ISO9001/Trading certificate/SGS/FormE)

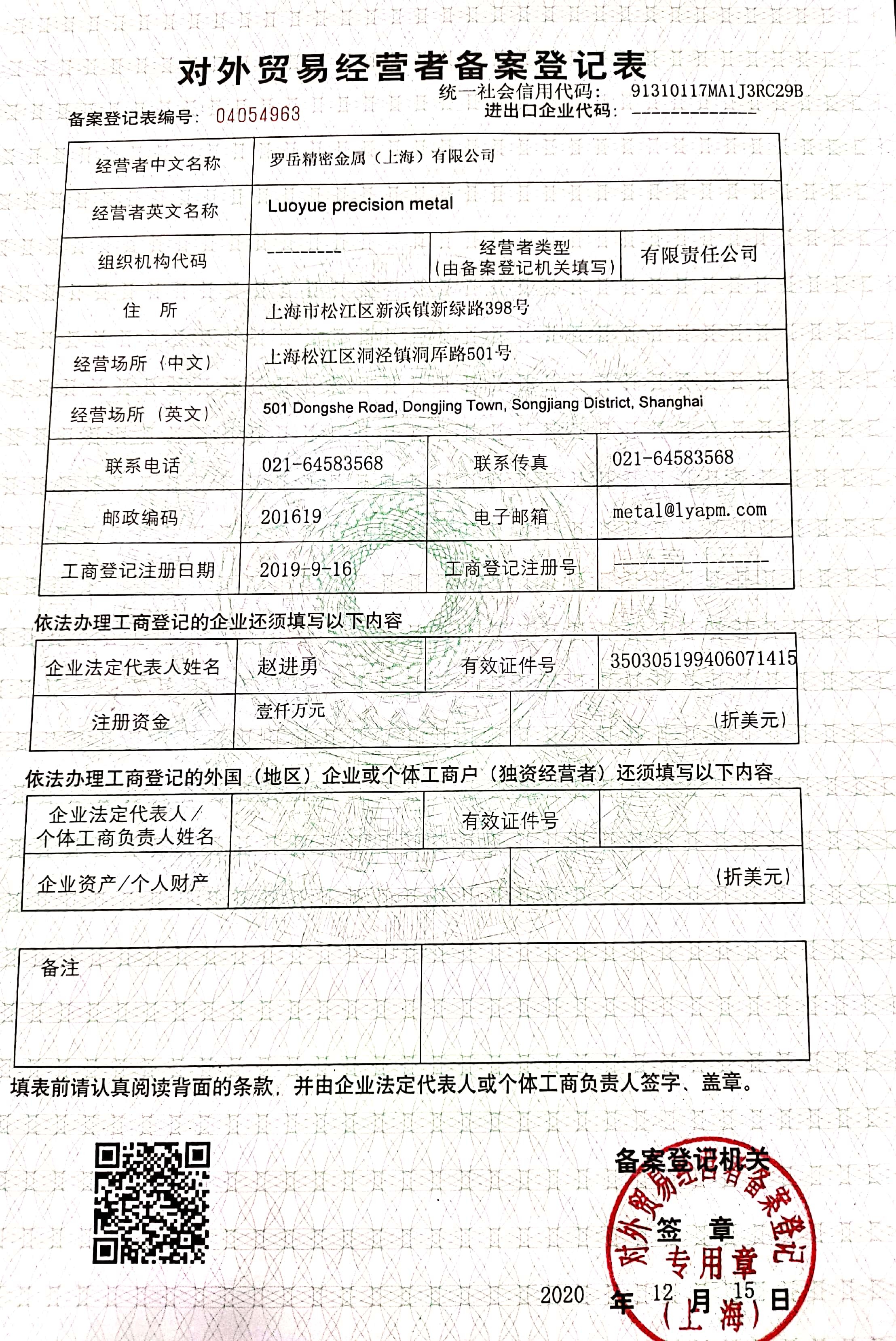 .
. 


3. Our customers

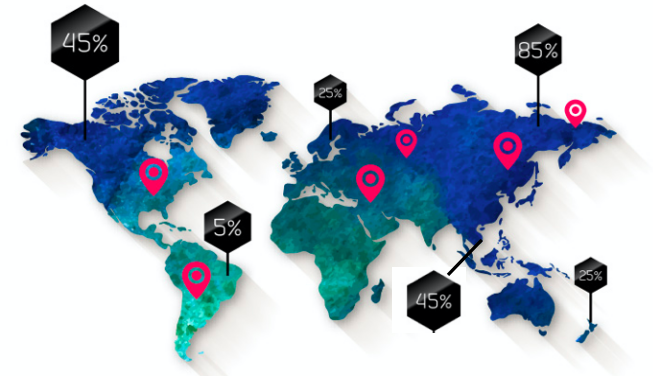
Customer visits



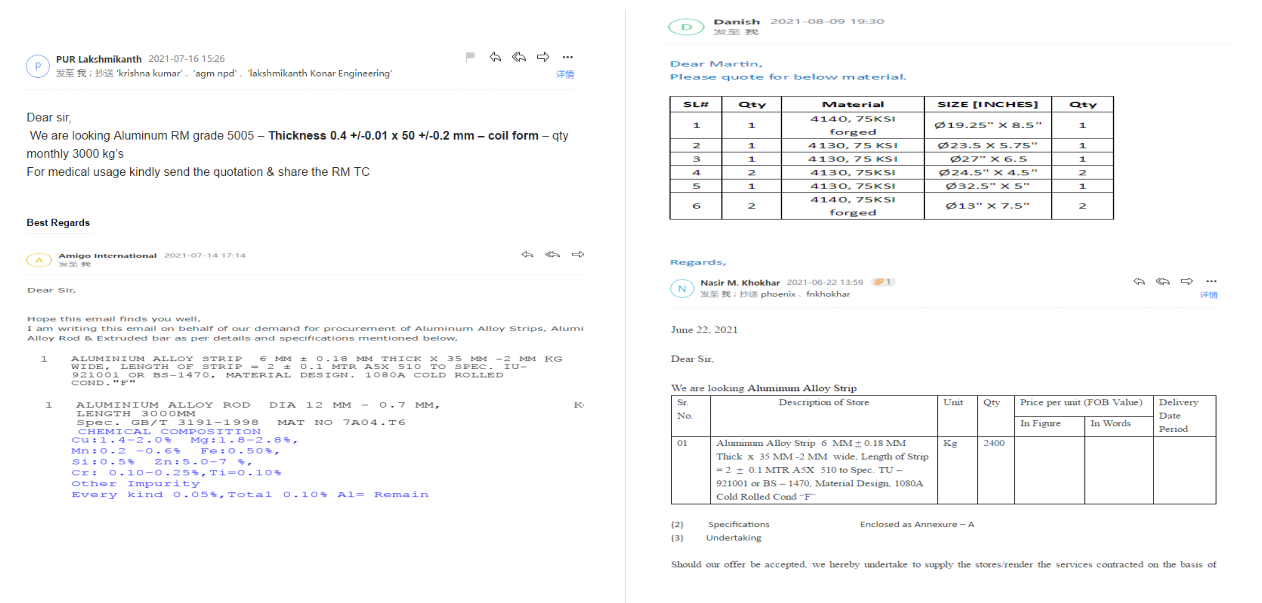
4. Past Inquiry
. 
1.Customer Rating
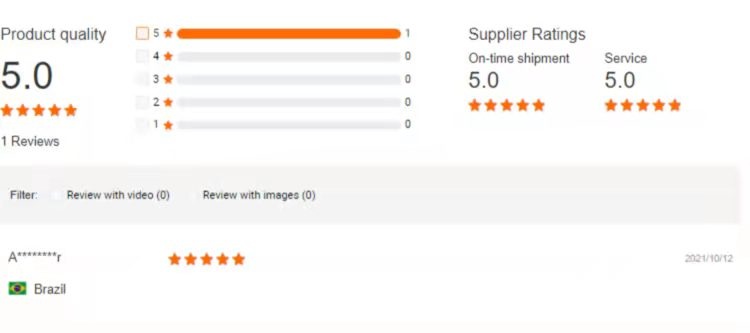
FAQ
1. Q: Are you a manufacturer?
A:No, we are not manufacturers. We have our own warehouse and our own company. I believe we will be the most suitable supplier for you.
2. Could we visit your factory?
A: Sure, we welcome you to visit the factory , check our production lines and know more about our strength and quality.
3. Q: Do you have quality control system?
A: Yes, we have ISO, BV, SGS certifications and our own quality control laboratory.
4. Q: Can you arrange the shipment for us?
A: Yes, we have designated sea freight and railway freight forwarders with decades of experiences and we get the best price with earliest vessel and professional service.
5. Q: How long is the delivery time?
A: Generally it is 7 days if we have the exact goods in our stock. If not, it will take around 15-20 days to get goods ready for delivery.
6. Q: Can I get some samples?
A: We are glad to provide free samples to you, but we do not offer the freight.
7. Q: What is your after-sale service?
A: We provide after-sale service and offer 100% guarantee on our products.
8. Q: What is your MOQ?
A: 2 Tons









 NO.501 Dongshe Road, Dongjing Town, Songjiang District, Shanghai,China,201600
NO.501 Dongshe Road, Dongjing Town, Songjiang District, Shanghai,China,201600 Mobile/Whatsapp/Zalo/Lines/Skype:+8616628500844
Mobile/Whatsapp/Zalo/Lines/Skype:+8616628500844